Tube expansion evaluation and measurement of processing for the “EXPANDER” tube expansion tool
Tube expansion process using the “Tube Expander”
Tube expansion evaluation and measurement
The appropriate amount of tube expansion for the Tube Expander differs depending on the dimensions of the tube sheet hole diameter, outer diameter of the tube, and tube thickness as well as the material of the tube.
The “tube thickness reduction rate” and “tube inner diameter growth rate” are the two general methods for measuring the degree of tube expansion.
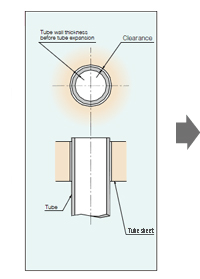
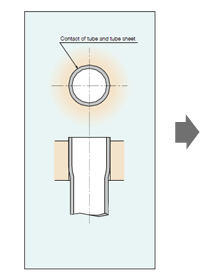
Before tube expansion
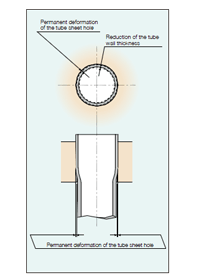
After tube expansion
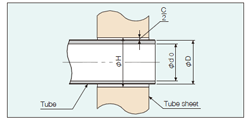
1. Calculation of the tube thickness reduction rate
Wt = ( ( D – d0 ) – ( H – d1 ) ) / ( D – d0 ) × 100
d1 = H – ( D – d0 ) × ( 1 – Wt / 100)
Wt: tube thickness reduction rate (%)
H: sheet hole diameter before tube expansion (mm)
D: outer diameter of tube before tube expansion (mm)
d0: inner diameter of tube before expansion (mm)
d1: inner diameter of tube after tube expansion (mm)
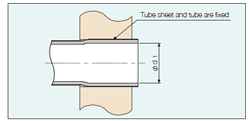
2. Calculation of tube inner diameter growth rate
Wd = ( d1 – ( d0 + C ) ) / ( d0 + C ) × 100
d1 = ( d0 + C ) × ( 1 + Wd / 100 )
In general, it is estimated that Wd is between 1 and 1.2%.
Wd: tube inner diameter growth rate (%)
d0 : inner diameter of tube before tube expansion (mm)
d1 : inner diameter of tube after tube expansion (mm)
C: space between sheet hole diameter and outer diameter of tube (mm) ( C = H – D )
Tube thickness reduction rate and residual contact pressure
| Tube sheet material | Tube material | Tube thickness reduction rate (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Steel | Steel | 7 |
| Steel | Copper | 5 |
| Copper | Copper | 10 |
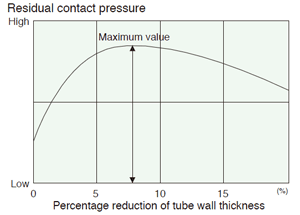
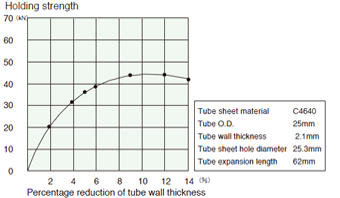
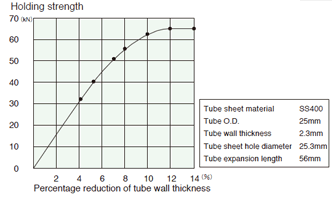
Tube thickness reduction rate and fixing strength
Tube material STB340
Tube material C6871